Memory cards are those little accessories you need for expand the storage of technological devices such as cell phones, cameras or camcorders.
They started out as a luxury accessory, but their price has been significantly reduced and they are now accessible to any user. Without going any further, it is very likely that you also have a memory card at home. Do you know what its main features are?
Maybe you have memory cards that you haven't used in a long time and you lack all the information about. You don't know what capacity they have, what is their reading speed or just what kind of memory card it is. If so, you don't need to worry, because with this guide you will learn a read the numbers and codes of your memory card to fully understand all its features.

This is all you need to know to read the numbers and codes on your memory card.
How to read numbers and codes from a memory card
If you analyze your memory card well, you will find several terms that are difficult to crack. Taking the model in the image above as an example, we see that it says the following: SanDisk Extreme, 128 GB, microSD, XC, V30, A2… What does all this mean?
It's easy, each of these terms refers to the main characteristics of your card, which we will discuss one by one below.
Creator
One of the terms more highlighted on the card is the name of the card manufacturer. In our example the brand is SanDisk, although memory cards can be from other brands such as Kingston, Trascend o Samsung.
Types of cards
Another term you will surely find informs you about the type of memory card you own. In summary, the card can be of two types: Compact Flash e SD (Secure Digital).
On the one hand, Compact Flash cards can be of type I or type II. On the other hand, SD memory cards can be simply SD, microSD or MiniSD, which have not been very successful on the market. If you look at your card, you will see that it says Compact Flash, SD or microSD, as is the case with the model we took as an example.
Memory capacity
The number which refers to the capacity of the card is also very important. We could say that it is the most relevant of all, because when we use these cards what matters mainly to us is the memory that we are going to add to the device in which we will use them.
The memory capacity of a card is represented in gigabytes and can be very varied: 32 GB, 64 GB, 128 GB, 256 GB… Obviously, the more capacity the card has, the more expensive it will be.
SD cards also represent their using capacity i termini SC, HC e XC, which mean the following:
- SC: Standard capacity, up to 2GB of memory.
- HC: high capacity, up to 32GB of memory.
- XC: Extended capacity, up to 2TB of storage.

Example of an XC microSD memory card.
Speed of reading and writing
Another of the codes that you will see on your memory card is the one that refers to the writing speed, also one of the characteristics that you should give more importance to when buying a new model. This is the how fast the card can store information. The higher the speed, the more information you can save in less time.
On some cards you will find the write speed directly, for example 50MB / s. This data refers to the maximum speed that the card can reach, but not to speed known as "minimum maintained", which is usually reflected in the form of different codes depending on the type of card.
First of all, remember that Compact Flash cards use terminology Ultra Direct Memory Access (UDMA), che va da 0 (16,7 MB/s) a 7 (167 MB/s).
In SD memory cards, however, you will need to pay attention to concept di "Class" to find out what their write speed is, in addition to take into account the Bus - data transfer system -. The different classes of an SD card are as follows:
- Class 2 (C2) - Minimum write speed of 2 MB / s.
- Class 4 (C4): minimum write speed of 4 MB / s.
- Class 6 (C6): minimum write speed of 6 MB / s.
- Class 10 (C10): minimum write speed of 10 MB / s.
These speeds were insufficient for SD cards, so the standard UHS (Ultra High Speed) class I and II, giving rise to UHS-I, UHS-I II, SDHC I, SDHC II, SDXC I and SDXC II cards. If we look at the SanDisk card we have chosen as an example, we can see that it is SDXC I.
Additionally, these types of cards use another term to indicate their minimum maintained write speed. They can be the following:
- Ultra High Speed Class I (U1): minimum write speed of 10MB / s, but better data transfer system than Class 10.
- Ultra High Speed Class 3 (U3): minimum write speed of 30 MB / s.
If you look closely at the example model in this guide, you will see that the code “V30” also appears, do you know what it refers to? Well, this term is related to video speed, so you mostly care if you use memory card in video cameras. You can find the following codes:
- Class V6: 72p HD video recording.
- Class V10: video recording in Full HD resolution at 1080p or lower.
- Class V30: video recording in 4K resolution at 24 or 30 fps.
- Class V60: video recording in 4K resolution at 60 or 120 fps.
- Class V90: video recording with 8K resolution at 60 or 120 fps.
It is also important to know that some memory cards indicate their reading speed, which is represented by codes such as “x300”, “x600” o “x1000”. The higher the amount, the faster your card can be read.
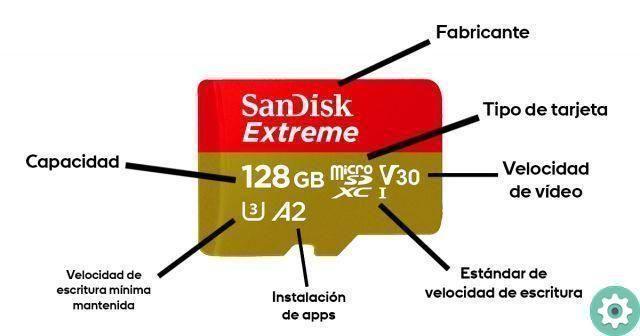
These are the meanings of the different codes and numbers on a memory card.
Compatibility with app installation
Since Android 6, users have the ability to install applications directly on microSD cards inserted in mobile phones. However, it wasn't the best possible option, as most microSDs weren't designed for this feature and ended up affect terminal performance.
For this reason, in August 2019 the first class A1 and A2 microSD memory cards arrived on the market, created specifically for Android users to install apps directly on them without affecting the performance of the phone.
Both A1 and A2 class cards support fast read and write speeds, with the minimum maintained speed of both 10 MB / s. Therefore, if you are going to use a microSD card in your mobile, make sure it has these specifications.
Finally, another aspect that you should consider before buying a memory card is the its strength and durability. This data is not reflected on the board itself, so if you have one at home and want to know its resistance level, you should go online to find out the information offered by the manufacturer about it.
Brands often test the durability of their cards by testing them under the toughest conditions. For example, in the case of our example, SanDisk specifies that it is resistant to high temperatures, water, X-rays and shocks.
This way, you will know that you can give your memory card continuous use without fearing it will damage easily and you will lose data which stores.
So far our guide on the meaning of numbers and codes that make up a memory card. You've already seen that at first they seem like a series of nonsense terms, but with a little theory they help you easily know the most important features of your memory card.