Services provide more security and are critical to the functioning of the entire operating system. These start when the computer starts and can respond to requests on the network or monitor the execution of system processes.
If you have a computer with two operating systems, you can change the Grub boot order in Ubuntu Linux.
Systemd and Systemctl
He is everyone's steward and services Linux and Systemctl no it is a special command. This will have the task of starting all those elements that need to be loaded once the system is started. It is a set of daemons and tools designed for configuring and interacting with the Linux kernel.
Systemd is like the parent of the processes, as its main goal is to merge all the basic distributions and configurations. It was created to replace the previous SysV system, going beyond simple startup tasks.
In addition to the Systemctl program manager, to make your programs run faster it is recommended that you free up space on your hard drive for more capacity.
System functionality
- He greatly improved his speed at the start of the program. Also, activate the services via “Socket” which is an application programming interface (API).
- You can register via “Cgroups” all those services and programs that have been started. Systemd comes with predefined packages, so you can run and manage multiple daemons in parallel.

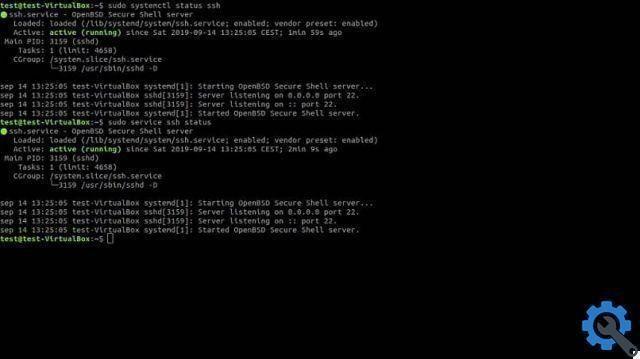
Systemd is used by most of the programs offered from Linux by default. From Fedora, Red Hat and Debian to Arch. And, with the Systemctl command, in addition to providing information on the status of Systemd and managing executions, you can manage Ubuntu Linux system services with Systemctl.
Manage Ubuntu Linux system services with Systemctl
With Systemctl you can start and stop a program, reload, activate and deactivate services, among other things. To start managing Ubuntu Linux system services with Systemctl you need to make sure you have it on your system.
From the internet you can search and download all the programs you need for your computer.
To do this, open the window "Terminal" and execute the command " Systemd - version ”With this you can know the version number installed on your Linux system.
Systemctl daemons or services
- Systemd - analyze, allows you to see the progress of the system startup. In addition to its qualities such as, the time it took to get started and what processes added time to this startup. To view each process individually, use the command " Systemd - analyze error ".
- " Systemctl list-unit-files ”Is a command used to view sections of files or drives. This is done because Systemd uses services, mount points and devices. So, with this command you can see each one and how they worked.
- " Systemctl list-unit-files - type = service ”Is used to know which services or daemons have been and are enabled and which others are not. It is quite similar to the previous command, but this adds the option to show only the list of services.

Other commands may be, “Systemctl is - active” is used to know which service is currently running. “Systemctl is - enable” is for daemons that are enabled or those that start automatically with the system.
- With " Systemctl is – fail ”You will be able to know if a problem has occurred at the beginning of the execution of a service. If the service doesn't work, you will get an on-screen message with the word "Failed". In case of unknown reasons, the message will be "Stranger" o "Idle".
By this you already know that Systemd has a large number of commands, even others that perform more complex functions. You can even restart, hibernate the system and even monitor the flow of energy consumed. This is a great start to manage i system services Ubuntu Linux con Systemctl.
Just like the Systemctl program allows you to start and stop a program, you can also program your Linux operating system to schedule it to turn on and off.
TagsLinux